[Python 100일 챌린지] Day 37 - 캡슐화와 정보 은닉 심화
은행 계좌 객체에서
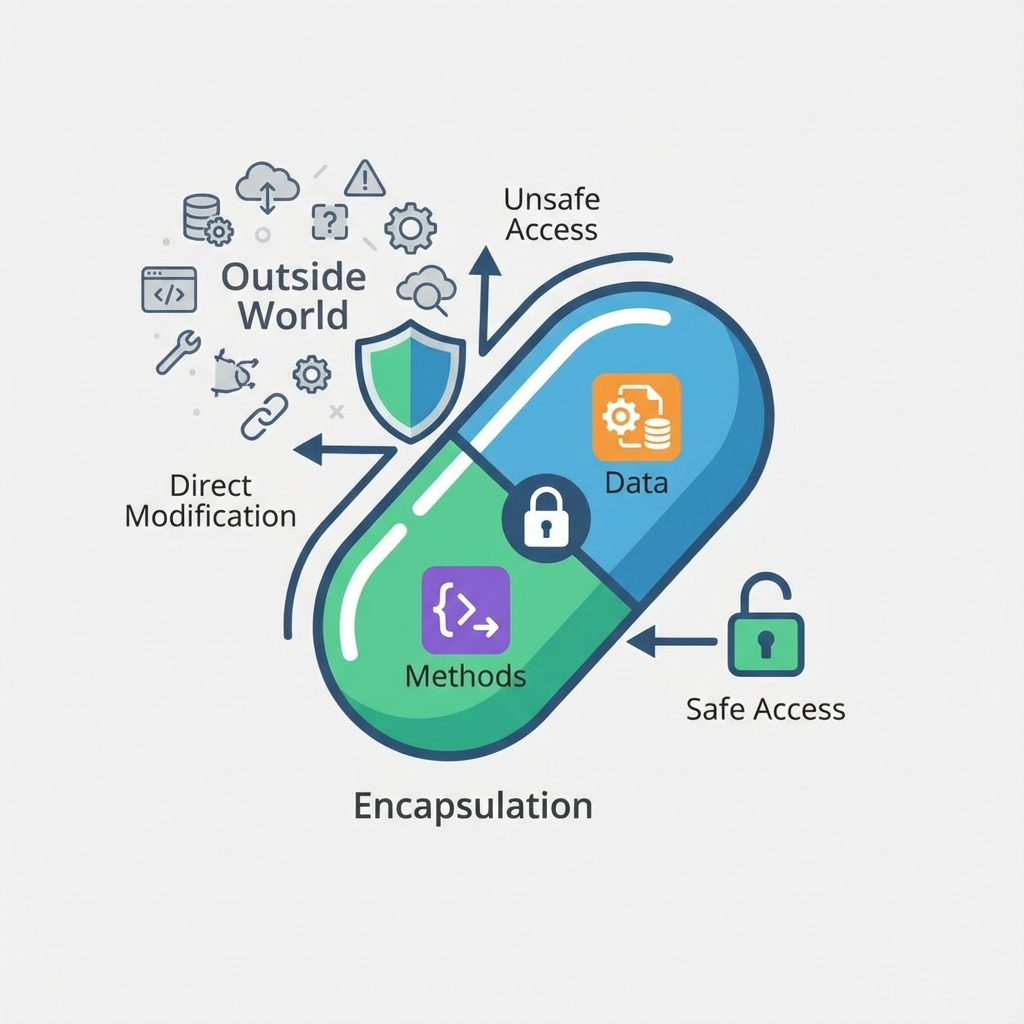
account.balance = -1000000이렇게 잔액을 음수로 바꿀 수 있다면 문제 아닐까요? 🤔 ──중요한 데이터를 아무렇게나 변경하지 못하도록 보호해야 합니다! 😊ATM을 생각해보세요. 현금을 직접 만질 수 없고, “출금” 버튼을 통해서만 안전하게 받습니다. 누군가 ATM을 뜯어서 돈을 마음대로 가져가면 안 되잖아요?
게임 캐릭터도 마찬가지입니다.
player.hp = 999999처럼 HP를 직접 조작하면 치트가 됩니다.heal(),damage()메서드를 통해서만 HP를 변경해야 공정하죠!이것이 캡슐화(Encapsulation)입니다! 데이터를 숨기고, 안전한 방법으로만 접근하게 만드는 OOP의 핵심 원리! 💡
🎯 오늘의 학습 목표
⭐⭐⭐⭐ (40-50분 완독)
📚 사전 지식
🎯 학습 목표 1: 캡슐화의 개념과 중요성 이해하기
Day 33에서 Private 변수와 Property의 기초를 배웠습니다. 오늘은 이를 더 깊이 파헤쳐, 실전에서 안전한 클래스를 설계하는 방법을 익힙니다!
캡슐화(Encapsulation)는 데이터와 메서드를 하나로 묶고, 외부 접근을 제한하는 OOP 핵심 원칙입니다.
🏥 실생활 비유: 약 캡슐
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 캡슐화 = 약을 캡슐에 넣는 것
class Medicine:
def __init__(self, name, dosage):
self.__name = name # Private - 직접 접근 불가
self.__dosage = dosage # Private - 직접 접근 불가
def take(self):
"""안전한 방법으로만 복용"""
if self.__dosage > 0:
print(f"{self.__name} 복용")
self.__dosage -= 1
else:
print("복용량 초과!")
medicine = Medicine("타이레놀", 3)
medicine.take() # ✅ 안전한 방법
# medicine.__dosage = 100 # ❌ 직접 접근 불가!
왜 캡슐화가 필요할까?
- 데이터 무결성 보장
- 잘못된 값 방지
- 내부 구현 변경 용이
🎯 학습 목표 2: 접근 제어자 사용법 배우기
Python의 3가지 접근 제어
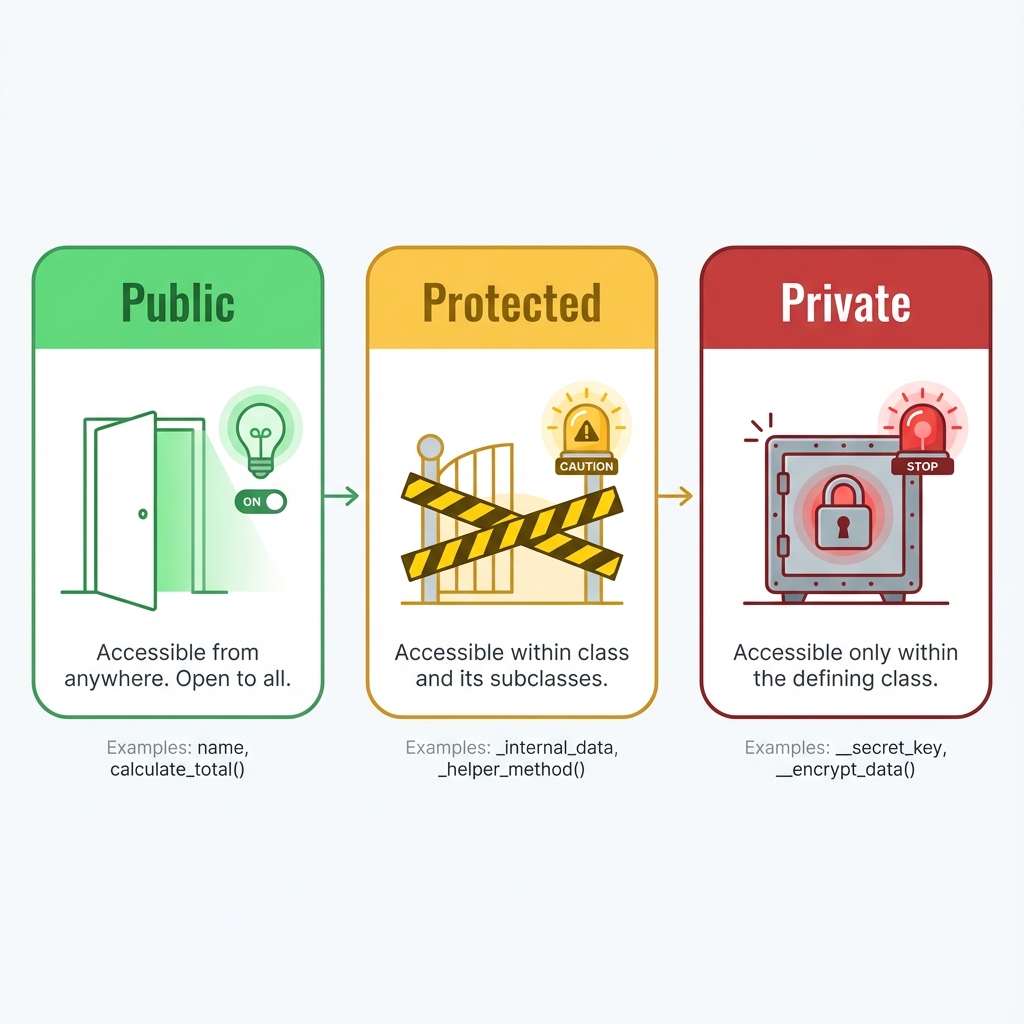 접근 제어자: Public, Protected, Private의 차이
접근 제어자: Public, Protected, Private의 차이
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class BankAccount:
def __init__(self, owner, balance):
self.owner = owner # Public
self._balance = balance # Protected
self.__pin = "1234" # Private
# Public 메서드
def deposit(self, amount):
self._balance += amount
# Protected 메서드
def _validate(self, pin):
return pin == self.__pin
# Private 메서드
def __encrypt(self, data):
return f"encrypted_{data}"
account = BankAccount("홍길동", 10000)
# Public - 어디서나 접근 가능
print(account.owner) # ✅ 홍길동
# Protected - 접근 가능하지만 권장하지 않음
print(account._balance) # ⚠️ 10000 (가능하지만 하지 마세요)
# Private - 접근 불가
# print(account.__pin) # ❌ AttributeError!
🎯 학습 목표 3: Property 데코레이터로 안전하게 속성 관리하기
읽기 전용 속성
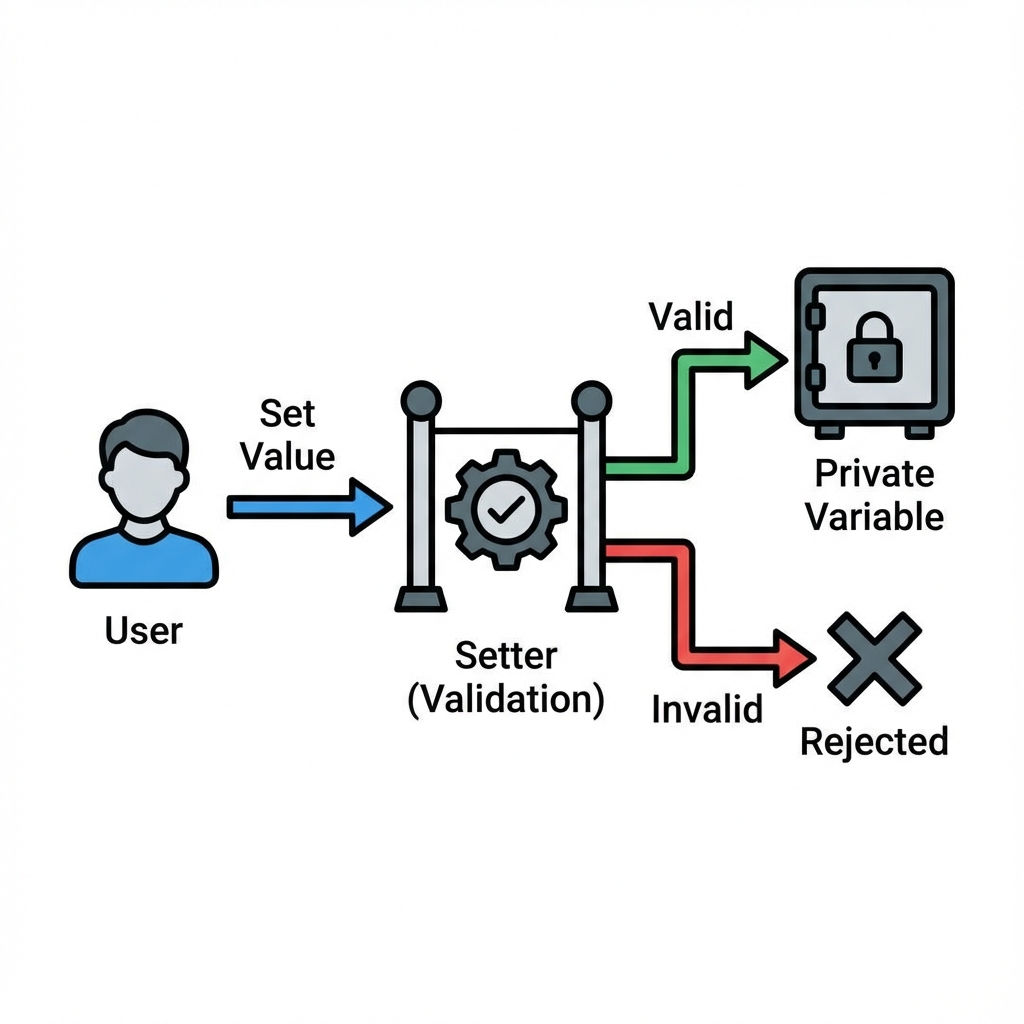 Property 흐름: Setter를 통한 유효성 검사
Property 흐름: Setter를 통한 유효성 검사
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class Circle:
def __init__(self, radius):
self._radius = radius
@property
def radius(self):
"""반지름 (읽기만 가능)"""
return self._radius
@property
def diameter(self):
"""지름 (계산된 읽기 전용)"""
return self._radius * 2
@property
def area(self):
"""넓이 (계산된 읽기 전용)"""
return 3.14159 * self._radius ** 2
circle = Circle(5)
print(f"반지름: {circle.radius}")
print(f"지름: {circle.diameter}")
print(f"넓이: {circle.area}")
# circle.area = 100 # ❌ AttributeError: can't set attribute
유효성 검사가 있는 Setter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self._name = name
self._age = age
@property
def age(self):
return self._age
@age.setter
def age(self, value):
"""나이 설정 (유효성 검사 포함)"""
if not isinstance(value, int):
raise TypeError("나이는 정수여야 합니다")
if value < 0:
raise ValueError("나이는 0 이상이어야 합니다")
if value > 150:
raise ValueError("나이가 너무 많습니다")
self._age = value
@property
def name(self):
return self._name
@name.setter
def name(self, value):
"""이름 설정 (유효성 검사 포함)"""
if not isinstance(value, str):
raise TypeError("이름은 문자열이어야 합니다")
if len(value.strip()) < 2:
raise ValueError("이름은 2자 이상이어야 합니다")
self._name = value.strip()
# 사용
person = Person("홍길동", 30)
print(person.name, person.age)
person.age = 31 # ✅ OK
# person.age = -5 # ❌ ValueError
# person.age = "삼십" # ❌ TypeError
Deleter 사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
class CachedData:
def __init__(self):
self._cache = None
@property
def data(self):
"""캐시된 데이터"""
if self._cache is None:
print("데이터 로딩 중...")
self._cache = "Heavy Data"
return self._cache
@data.deleter
def data(self):
"""캐시 삭제"""
print("캐시 삭제됨")
self._cache = None
obj = CachedData()
print(obj.data) # 데이터 로딩 중... Heavy Data
print(obj.data) # Heavy Data (캐시됨)
del obj.data # 캐시 삭제됨
print(obj.data) # 데이터 로딩 중... Heavy Data (다시 로딩)
🎯 학습 목표 4: 불변 객체와 실전 패턴 익히기
불변 객체 (Immutable Object)
한번 생성되면 변경할 수 없는 객체입니다.
💡 고급 개념 미리보기
아래 코드에서
__slots__와object.__setattr__는 고급 기법입니다.
__slots__: 클래스가 가질 수 있는 속성을 미리 지정해서, 새로운 속성 추가를 막습니다object.__setattr__: 우리가 만든__setattr__를 우회해서 초기값을 설정하는 트릭입니다지금은 “이렇게 하면 수정 불가능한 객체를 만들 수 있구나!” 정도로 이해하면 충분합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
class ImmutablePoint:
"""불변 좌표 클래스"""
__slots__ = ('_x', '_y') # 이 속성들만 허용, 다른 속성 추가 불가
def __init__(self, x, y):
# object.__setattr__: __setattr__ 오버라이드를 우회하여 초기값 설정
object.__setattr__(self, '_x', x)
object.__setattr__(self, '_y', y)
@property
def x(self):
return self._x
@property
def y(self):
return self._y
def __setattr__(self, name, value):
raise AttributeError("불변 객체는 수정할 수 없습니다")
def __delattr__(self, name):
raise AttributeError("불변 객체는 삭제할 수 없습니다")
def move(self, dx, dy):
"""새로운 불변 객체 반환"""
return ImmutablePoint(self._x + dx, self._y + dy)
def __repr__(self):
return f"Point({self._x}, {self._y})"
# 사용
point1 = ImmutablePoint(10, 20)
print(point1) # Point(10, 20)
# ❌ 수정 불가
# point1.x = 30 # AttributeError
# ✅ 새 객체 생성
point2 = point1.move(5, 5)
print(point1) # Point(10, 20) (원본 유지)
print(point2) # Point(15, 25) (새 객체)
🎯 학습 목표 5: 실전 예제로 종합 정리하기
은행 계좌 시스템
💡 타입 힌트란?
List[Dict]나owner: str처럼 변수 타입을 명시하는 것을 타입 힌트라고 합니다. Python은 타입 힌트가 없어도 동작하지만, 코드 가독성과 IDE 자동완성에 도움이 됩니다. 지금은 무시해도 괜찮습니다!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
from datetime import datetime
from typing import List, Dict # 타입 힌트용 (선택 사항)
class BankAccount:
"""안전한 은행 계좌 클래스"""
# 클래스 변수
_account_count = 0
INTEREST_RATE = 0.02
def __init__(self, owner: str, initial_balance: float = 0):
# Private 변수
self.__owner = owner
self.__balance = 0
self.__pin = None
self.__transactions: List[Dict] = []
self.__account_number = self.__generate_account_number()
# 초기 입금
if initial_balance > 0:
self.deposit(initial_balance)
@classmethod
def __generate_account_number(cls):
"""계좌번호 생성 (Private)"""
cls._account_count += 1
return f"ACC{cls._account_count:06d}"
# Public Property - owner (읽기 전용)
@property
def owner(self) -> str:
return self.__owner
# Public Property - balance (읽기 전용)
@property
def balance(self) -> float:
return self.__balance
# Public Property - account_number (읽기 전용)
@property
def account_number(self) -> str:
return self.__account_number
# Private 메서드
def __record_transaction(self, transaction_type: str, amount: float):
"""거래 기록 (Private)"""
self.__transactions.append({
'type': transaction_type,
'amount': amount,
'balance': self.__balance,
'timestamp': datetime.now()
})
# Public 메서드
def deposit(self, amount: float) -> str:
"""입금"""
if amount <= 0:
raise ValueError("입금액은 0보다 커야 합니다")
self.__balance += amount
self.__record_transaction('입금', amount)
return f"✅ {amount:,}원 입금 완료 (잔액: {self.__balance:,}원)"
def withdraw(self, amount: float, pin: str = None) -> str:
"""출금 (PIN 필요)"""
if amount <= 0:
raise ValueError("출금액은 0보다 커야 합니다")
# PIN 확인 (설정된 경우)
if self.__pin and not self.__verify_pin(pin):
raise PermissionError("PIN이 일치하지 않습니다")
if amount > self.__balance:
raise ValueError(f"잔액 부족 (현재 잔액: {self.__balance:,}원)")
self.__balance -= amount
self.__record_transaction('출금', amount)
return f"✅ {amount:,}원 출금 완료 (잔액: {self.__balance:,}원)"
def set_pin(self, new_pin: str):
"""PIN 설정"""
if not isinstance(new_pin, str) or len(new_pin) != 4:
raise ValueError("PIN은 4자리 문자열이어야 합니다")
if not new_pin.isdigit():
raise ValueError("PIN은 숫자만 가능합니다")
self.__pin = new_pin
return "✅ PIN이 설정되었습니다"
def __verify_pin(self, pin: str) -> bool:
"""PIN 검증 (Private)"""
return pin == self.__pin
def apply_interest(self):
"""이자 적용"""
interest = self.__balance * self.INTEREST_RATE
self.__balance += interest
self.__record_transaction('이자', interest)
return f"💰 이자 {interest:,}원 지급 (잔액: {self.__balance:,}원)"
def get_transaction_history(self, limit: int = 5) -> List[Dict]:
"""최근 거래 내역 조회"""
return self.__transactions[-limit:]
def print_statement(self):
"""계좌 명세서 출력"""
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"계좌 명세서")
print(f"{'='*60}")
print(f"계좌번호: {self.__account_number}")
print(f"예금주: {self.__owner}")
print(f"현재 잔액: {self.__balance:,}원")
print(f"{'-'*60}")
if self.__transactions:
print("최근 거래 내역:")
for i, trans in enumerate(self.__transactions[-5:], 1):
time = trans['timestamp'].strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
print(f"{i}. [{time}] {trans['type']}: {trans['amount']:,}원 "
f"(잔액: {trans['balance']:,}원)")
else:
print("거래 내역이 없습니다.")
print(f"{'='*60}\n")
# 사용 예시
account = BankAccount("홍길동", 1000000)
account.set_pin("1234")
print(account.deposit(500000))
print(account.withdraw(200000, "1234"))
print(account.apply_interest())
account.print_statement()
# 읽기 전용 속성
print(f"예금주: {account.owner}")
print(f"계좌번호: {account.account_number}")
print(f"잔액: {account.balance:,}원")
# ❌ 직접 수정 불가
# account.balance = 999999 # AttributeError
# account.__pin = "0000" # AttributeError
실행 결과:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
✅ 1,000,000원 입금 완료 (잔액: 1,000,000원)
✅ 500,000원 입금 완료 (잔액: 1,500,000원)
✅ 200,000원 출금 완료 (잔액: 1,300,000원)
💰 이자 26,000원 지급 (잔액: 1,326,000원)
============================================================
계좌 명세서
============================================================
계좌번호: ACC000001
예금주: 홍길동
현재 잔액: 1,326,000원
------------------------------------------------------------
최근 거래 내역:
1. [2025-04-06 10:00:00] 입금: 1,000,000원 (잔액: 1,000,000원)
2. [2025-04-06 10:00:01] 입금: 500,000원 (잔액: 1,500,000원)
3. [2025-04-06 10:00:02] 출금: 200,000원 (잔액: 1,300,000원)
4. [2025-04-06 10:00:03] 이자: 26,000원 (잔액: 1,326,000원)
============================================================
예금주: 홍길동
계좌번호: ACC000001
잔액: 1,326,000원
🧪 연습 문제
문제 1: 안전한 비밀번호 관리자
다음 요구사항을 만족하는 PasswordManager 클래스를 작성하세요:
요구사항:
- 비밀번호는 Private 변수로 해싱하여 저장
- 최소 8자, 대문자/소문자/숫자 포함 검증
- 비밀번호 변경 시 이전 비밀번호 확인 필요
- 로그인 시도 횟수 제한 (5회)
✅ 정답
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
import hashlib
class PasswordManager:
"""안전한 비밀번호 관리자"""
MAX_LOGIN_ATTEMPTS = 5
def __init__(self, username):
self.__username = username
self.__password_hash = None
self.__login_attempts = 0
self.__is_locked = False
def __hash_password(self, password):
"""비밀번호 해싱 (Private)"""
return hashlib.sha256(password.encode()).hexdigest()
def __validate_password(self, password):
"""비밀번호 유효성 검사 (Private)"""
if len(password) < 8:
raise ValueError("비밀번호는 최소 8자 이상이어야 합니다")
has_upper = any(c.isupper() for c in password)
has_lower = any(c.islower() for c in password)
has_digit = any(c.isdigit() for c in password)
if not (has_upper and has_lower and has_digit):
raise ValueError("대문자, 소문자, 숫자를 모두 포함해야 합니다")
def set_password(self, password):
"""초기 비밀번호 설정"""
if self.__password_hash is not None:
raise PermissionError("비밀번호 변경은 change_password()를 사용하세요")
self.__validate_password(password)
self.__password_hash = self.__hash_password(password)
return "✅ 비밀번호가 설정되었습니다"
def change_password(self, old_password, new_password):
"""비밀번호 변경"""
if not self.login(old_password):
raise PermissionError("현재 비밀번호가 일치하지 않습니다")
self.__validate_password(new_password)
self.__password_hash = self.__hash_password(new_password)
self.__login_attempts = 0
return "✅ 비밀번호가 변경되었습니다"
def login(self, password):
"""로그인"""
if self.__is_locked:
raise PermissionError("계정이 잠겼습니다. 관리자에게 문의하세요")
if self.__hash_password(password) == self.__password_hash:
self.__login_attempts = 0
return True
else:
self.__login_attempts += 1
remaining = self.MAX_LOGIN_ATTEMPTS - self.__login_attempts
if remaining == 0:
self.__is_locked = True
raise PermissionError("계정이 잠겼습니다")
print(f"❌ 비밀번호가 틀렸습니다 (남은 시도: {remaining}회)")
return False
@property
def username(self):
return self.__username
@property
def is_locked(self):
return self.__is_locked
# 테스트
pm = PasswordManager("user123")
print(pm.set_password("MyPass123"))
# 로그인 시도
print(pm.login("WrongPass")) # False
print(pm.login("MyPass123")) # True
# 비밀번호 변경
print(pm.change_password("MyPass123", "NewPass456"))
문제 2: 안전한 온도 조절기
다음 요구사항을 만족하는 Thermostat 클래스를 작성하세요:
요구사항:
- 온도는 Private 변수로 저장
- 온도 범위 제한: 10°C ~ 30°C
- 현재 온도는 읽기 전용
- 온도 조절은
increase(),decrease()메서드로만 가능 (1도씩)
1
2
3
4
5
# 사용 예시
thermostat = Thermostat(20)
print(thermostat.temperature) # 20
thermostat.increase()
print(thermostat.temperature) # 21
💡 힌트
@property로 읽기 전용 속성을 만드세요increase()와decrease()메서드 내에서 범위 검사를 하세요- Private 변수는
self.__temperature로 선언하세요
✅ 정답
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
class Thermostat:
"""안전한 온도 조절기"""
MIN_TEMP = 10
MAX_TEMP = 30
def __init__(self, initial_temp=20):
# Private 변수
self.__temperature = initial_temp
# 초기값 검증
if not (self.MIN_TEMP <= initial_temp <= self.MAX_TEMP):
self.__temperature = 20
print(f"⚠️ 유효하지 않은 초기값. 기본값 20°C로 설정됩니다.")
@property
def temperature(self):
"""현재 온도 (읽기 전용)"""
return self.__temperature
def increase(self):
"""온도 1도 올리기"""
if self.__temperature >= self.MAX_TEMP:
print(f"❌ 최대 온도({self.MAX_TEMP}°C)에 도달했습니다")
return
self.__temperature += 1
print(f"🔺 온도 상승: {self.__temperature}°C")
def decrease(self):
"""온도 1도 내리기"""
if self.__temperature <= self.MIN_TEMP:
print(f"❌ 최소 온도({self.MIN_TEMP}°C)에 도달했습니다")
return
self.__temperature -= 1
print(f"🔻 온도 하강: {self.__temperature}°C")
def __str__(self):
return f"현재 온도: {self.__temperature}°C"
# 테스트
thermostat = Thermostat(20)
print(thermostat) # 현재 온도: 20°C
thermostat.increase() # 🔺 온도 상승: 21°C
thermostat.increase() # 🔺 온도 상승: 22°C
thermostat.decrease() # 🔻 온도 하강: 21°C
# 읽기 전용 확인
print(f"현재 온도: {thermostat.temperature}°C") # 21°C
# ❌ 직접 수정 불가
# thermostat.temperature = 100 # AttributeError!
# thermostat.__temperature = 100 # 동작하지 않음 (Name Mangling)
# 경계값 테스트
hot = Thermostat(30)
hot.increase() # ❌ 최대 온도(30°C)에 도달했습니다
cold = Thermostat(10)
cold.decrease() # ❌ 최소 온도(10°C)에 도달했습니다
💡 실전 팁 & 주의사항
Tip 1: Private 변수와 Public Property 조합
중요한 데이터는 Private 변수로 보호하고, Property로 안전하게 접근하세요.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# ✅ 권장 패턴
class GoodExample:
def __init__(self, value):
self.__value = value # Private
@property
def value(self):
return self.__value
@value.setter
def value(self, new_value):
if new_value < 0:
raise ValueError("값은 0 이상이어야 합니다")
self.__value = new_value
Tip 2: 유효성 검사는 Setter에서
속성 값을 변경할 때 검증 로직은 Setter 메서드에 구현하세요.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
@property
def age(self):
return self.__age
@age.setter
def age(self, value):
if not isinstance(value, int):
raise TypeError("나이는 정수여야 합니다")
if value < 0 or value > 150:
raise ValueError("유효하지 않은 나이입니다")
self.__age = value
Tip 3: 읽기 전용 속성 활용
변경되면 안 되는 속성은 Setter 없이 Property만 구현하세요.
1
2
3
4
5
6
@property
def created_at(self):
"""생성 시간 (읽기 전용)"""
return self.__created_at
# Setter 없음 - 변경 불가!
📝 오늘 배운 내용 정리
| 개념 | 설명 | 사용 시기 |
|---|---|---|
| Public | self.attr | 외부 접근 필요 |
| Protected | self._attr | 내부용이지만 상속 허용 |
| Private | self.__attr | 완전히 숨김 |
| @property | Getter | 읽기 전용 또는 계산 |
| @attr.setter | Setter | 유효성 검사 필요 |
| 불변 객체 | 수정 불가 | 안전성 최우선 |
캡슐화 베스트 프랙티스
✅ 권장:
- Private 변수 + Public Property
- 유효성 검사는 Setter에서
- 계산된 값은 읽기 전용 Property
- 민감한 데이터는 반드시 Private
❌ 주의:
- Public 변수로 모든 것 노출
- 유효성 검사 없는 Setter
- Name Mangling 우회 시도
🔗 관련 자료
📚 이전 학습
Day 36: 메서드 오버라이딩과 다중 상속 ⭐⭐⭐⭐
어제는 메서드 오버라이딩 심화, 다중 상속과 MRO, 믹스인(Mixin) 패턴을 배웠습니다!
📚 다음 학습
Day 38: 다형성(Polymorphism) ⭐⭐⭐⭐
내일은 다형성의 개념, 덕 타이핑(Duck Typing), 연산자 오버로딩, 추상 베이스 클래스(ABC)를 배웁니다!
“늦었다고 생각할 때가 가장 빠른 시기입니다!” 🚀
Day 37/100 Phase 4: 객체지향 프로그래밍 #100DaysOfPython