image: path: /assets/img/posts/python/python-mastery-03-conditionals-loops.png alt: Python 조건문과 반복문
🎮 5분 만에 게임 만들며 배우기
숫자 맞추기 게임
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| import random
def number_guessing_game():
"""조건문과 반복문을 활용한 숫자 맞추기 게임"""
secret = random.randint(1, 100)
attempts = 0
max_attempts = 10
print("🎲 1부터 100 사이의 숫자를 맞춰보세요!")
print(f"기회는 {max_attempts}번입니다.\n")
while attempts < max_attempts:
attempts += 1
# 입력 받기
try:
guess = int(input(f"시도 {attempts}/{max_attempts}: "))
except ValueError:
print("❌ 숫자를 입력해주세요!")
continue
# 범위 체크
if guess < 1 or guess > 100:
print("⚠️ 1부터 100 사이의 숫자를 입력하세요")
continue
# 정답 체크
if guess == secret:
print(f"\n🎉 정답입니다! {attempts}번 만에 맞추셨네요!")
if attempts <= 3:
print("👏 천재이십니다!")
elif attempts <= 7:
print("😊 잘하셨어요!")
else:
print("😅 아슬아슬했네요!")
break
elif guess < secret:
print("📈 더 큰 숫자입니다")
else:
print("📉 더 작은 숫자입니다")
# 남은 기회 알림
remaining = max_attempts - attempts
if remaining > 0:
print(f"남은 기회: {remaining}번")
else:
print(f"\n💔 실패! 정답은 {secret}였습니다")
# 게임 실행
# number_guessing_game()
|
🔀 프로그램의 흐름 제어
프로그램은 단순히 위에서 아래로만 실행되지 않습니다. 조건에 따라 다른 경로를 선택하거나, 특정 작업을 반복해야 할 때가 있습니다. 이번 포스트에서는 Python의 조건문과 반복문을 완벽히 마스터해보겠습니다.
조건문은 갈림길, 반복문은 회전교차로와 같습니다. 프로그램의 흐름을 자유자재로 제어해보세요!
📋 조건문 (Conditional Statements)
🏦 실무 예제: 대출 자격 심사 시스템
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| def loan_eligibility_check():
"""실제 은행에서 사용하는 대출 자격 심사"""
print("=" * 50)
print("대출 자격 심사 시스템".center(50))
print("=" * 50)
# 고객 정보 입력
age = 30
annual_income = 45000000 # 연소득 (원)
credit_score = 720 # 신용점수 (300-850)
employment_years = 3 # 근속연수
has_collateral = True # 담보 여부
existing_loans = 1 # 기존 대출 건수
# 대출 조건 심사
eligible = True
reasons = []
loan_limit = 0
interest_rate = 5.0 # 기본 금리
# 나이 조건 (20-65세)
if age < 20:
eligible = False
reasons.append("미성년자 대출 불가")
elif age > 65:
eligible = False
reasons.append("만 65세 초과")
# 연소득 조건 (2천만원 이상)
if annual_income < 20000000:
eligible = False
reasons.append("최소 연소득 미달")
else:
# 소득에 따른 대출 한도 설정
if annual_income >= 100000000:
loan_limit = annual_income * 5
interest_rate -= 1.0 # 우대 금리
elif annual_income >= 50000000:
loan_limit = annual_income * 4
interest_rate -= 0.5
else:
loan_limit = annual_income * 3
# 신용점수 평가
if credit_score < 600:
eligible = False
reasons.append("신용점수 부족")
elif credit_score >= 750:
interest_rate -= 0.5 # 우수 신용자 우대
# 근속연수 평가
if employment_years < 1:
eligible = False
reasons.append("근속기간 부족")
elif employment_years >= 5:
interest_rate -= 0.3 # 장기 근속자 우대
# 담보 여부에 따른 조정
if has_collateral:
loan_limit *= 1.5
interest_rate -= 0.5
# 기존 대출 건수 확인
if existing_loans >= 3:
eligible = False
reasons.append("과다 대출")
# 결과 출력
print(f"\n[고객 정보]")
print(f"나이: {age}세")
print(f"연소득: {annual_income:,}원")
print(f"신용점수: {credit_score}점")
print(f"근속연수: {employment_years}년")
print(f"담보: {'있음' if has_collateral else '없음'}")
print(f"기존대출: {existing_loans}건")
print(f"\n[심사 결과]")
if eligible:
print(f"✅ 대출 승인")
print(f"최대 대출 한도: {loan_limit:,.0f}원")
print(f"적용 금리: {interest_rate:.1f}%")
# 월 상환액 계산 (원리금 균등상환, 10년 기준)
monthly_rate = interest_rate / 100 / 12
months = 120 # 10년
if loan_limit > 0:
monthly_payment = (loan_limit * monthly_rate * (1 + monthly_rate)**months) / ((1 + monthly_rate)**months - 1)
print(f"예상 월 상환액: {monthly_payment:,.0f}원 (10년 기준)")
else:
print(f"❌ 대출 거절")
print(f"사유:")
for reason in reasons:
print(f" - {reason}")
# 실행
# loan_eligibility_check()
|
if 문의 기본 구조
Python의 if 문은 들여쓰기로 코드 블록을 구분합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| # 기본 if 문
age = 20
if age >= 18:
print("성인입니다")
print("투표권이 있습니다")
# if-else 문
score = 75
if score >= 80:
print("합격")
else:
print("불합격")
# if-elif-else 문
score = 85
if score >= 90:
grade = "A"
elif score >= 80:
grade = "B"
elif score >= 70:
grade = "C"
elif score >= 60:
grade = "D"
else:
grade = "F"
print(f"학점: {grade}")
|
중첩 조건문
조건문 안에 또 다른 조건문을 포함할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| # 중첩 if 문
age = 25
has_license = True
if age >= 18:
if has_license:
print("운전 가능")
else:
print("면허 필요")
else:
print("미성년자는 운전 불가")
# 논리 연산자로 단순화
if age >= 18 and has_license:
print("운전 가능")
elif age >= 18 and not has_license:
print("면허 필요")
else:
print("미성년자는 운전 불가")
|
삼항 연산자 (Ternary Operator)
간단한 조건문을 한 줄로 작성할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| # 기본 형태: 값1 if 조건 else 값2
age = 20
status = "성인" if age >= 18 else "미성년"
print(status) # "성인"
# 중첩 삼항 연산자 (가독성 주의)
score = 85
grade = "A" if score >= 90 else ("B" if score >= 80 else "C")
# 리스트 컴프리헨션에서 활용
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
result = ["짝수" if n % 2 == 0 else "홀수" for n in numbers]
print(result) # ['홀수', '짝수', '홀수', '짝수', '홀수']
|
match 문 (Python 3.10+)
Python 3.10부터 도입된 패턴 매칭 기능입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| # 기본 match 문
command = "start"
match command:
case "start":
print("프로그램 시작")
case "stop":
print("프로그램 종료")
case "pause":
print("일시 정지")
case _: # 기본값 (else와 같은 역할)
print("알 수 없는 명령")
# 패턴 매칭 활용
point = (0, 10)
match point:
case (0, 0):
print("원점")
case (0, y):
print(f"y축 위의 점: y={y}")
case (x, 0):
print(f"x축 위의 점: x={x}")
case (x, y):
print(f"좌표: ({x}, {y})")
# 가드 조건 사용
number = 15
match number:
case n if n < 0:
print("음수")
case n if n == 0:
print("영")
case n if n > 0 and n < 10:
print("한 자리 양수")
case _:
print("두 자리 이상의 양수")
|
🔄 반복문 (Loops)
💰 실무 예제: 주식 투자 시뮬레이터
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
| def stock_trading_simulator():
"""반복문을 활용한 주식 투자 시뮬레이션"""
import random
# 초기 설정
initial_money = 1000000 # 100만원
money = initial_money
stocks = 0
stock_price = 50000 # 초기 주가
days = 20
prices = []
portfolio = []
print("📈 20일간 주식 투자 시뮬레이션")
print(f"초기 자금: {initial_money:,}원")
print(f"초기 주가: {stock_price:,}원\n")
for day in range(1, days + 1):
# 주가 변동 (-10% ~ +10%)
change = random.uniform(-0.1, 0.1)
stock_price = int(stock_price * (1 + change))
prices.append(stock_price)
print(f"Day {day:2d}: 주가 {stock_price:,}원", end="")
# 매매 전략 (이동평균 기반)
if len(prices) >= 5:
avg_5 = sum(prices[-5:]) / 5
if stock_price < avg_5 * 0.95 and money >= stock_price:
# 5일 평균보다 5% 낮으면 매수
buy_qty = money // stock_price
if buy_qty > 0:
stocks += buy_qty
money -= buy_qty * stock_price
print(f" → 🔵 매수 {buy_qty}주", end="")
elif stock_price > avg_5 * 1.05 and stocks > 0:
# 5일 평균보다 5% 높으면 매도
sell_qty = stocks
money += sell_qty * stock_price
stocks -= sell_qty
print(f" → 🔴 매도 {sell_qty}주", end="")
# 포트폴리오 기록
total_value = money + stocks * stock_price
portfolio.append(total_value)
print(f" | 평가액: {total_value:,}원")
# 최종 결과
final_value = money + stocks * stock_price
profit = final_value - initial_money
profit_rate = (profit / initial_money) * 100
print(f"\n{'='*50}")
print("📊 투자 결과:")
print(f"최종 현금: {money:,}원")
print(f"보유 주식: {stocks}주 (평가액: {stocks * stock_price:,}원)")
print(f"총 자산: {final_value:,}원")
print(f"수익: {profit:,}원 ({profit_rate:+.1f}%)")
if profit > 0:
print("🎉 수익 달성!")
elif profit < 0:
print("😢 손실 발생")
else:
print("😐 본전")
# 실행
# stock_trading_simulator()
|
for 문
정해진 횟수만큼 반복하거나 시퀀스를 순회할 때 사용합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| # 리스트 순회
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
for fruit in fruits:
print(f"I like {fruit}")
# range() 함수 활용
# range(stop): 0부터 stop-1까지
for i in range(5):
print(i) # 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
# range(start, stop): start부터 stop-1까지
for i in range(2, 7):
print(i) # 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
# range(start, stop, step): step만큼 증가
for i in range(0, 10, 2):
print(i) # 0, 2, 4, 6, 8
# 역순 반복
for i in range(10, 0, -1):
print(i) # 10, 9, 8, ..., 1
|
enumerate()와 zip()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| # enumerate(): 인덱스와 값을 함께 반환
languages = ["Python", "Java", "C++"]
for idx, lang in enumerate(languages):
print(f"{idx + 1}. {lang}")
# 시작 인덱스 지정
for idx, lang in enumerate(languages, start=1):
print(f"{idx}. {lang}")
# zip(): 여러 시퀀스를 병렬로 순회
names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
ages = [25, 30, 35]
cities = ["Seoul", "Busan", "Daegu"]
for name, age, city in zip(names, ages, cities):
print(f"{name}({age})은 {city}에 삽니다")
# 길이가 다른 경우
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
letters = ['a', 'b', 'c']
for num, letter in zip(numbers, letters):
print(f"{num}: {letter}") # 짧은 쪽에 맞춰서 종료
|
while 문
조건이 참인 동안 계속 반복합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| # 기본 while 문
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(f"Count: {count}")
count += 1
# 무한 루프 (주의!)
# while True:
# user_input = input("종료하려면 'q' 입력: ")
# if user_input.lower() == 'q':
# break
# 조건 확인
password = ""
while len(password) < 8:
password = input("8자 이상의 비밀번호 입력: ")
print("비밀번호 설정 완료")
|
[!WARNING] 무한 루프 주의!
while True: 처럼 조건이 항상 참이면 반복문이 영원히 끝나지 않습니다. 반드시 break 문을 사용하거나 조건을 변경하여 루프를 탈출할 수 있는 구멍을 만들어주어야 합니다. 만약 프로그램이 멈추지 않는다면 Ctrl + C를 눌러 강제로 종료하세요!
break와 continue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| # break: 루프를 완전히 종료
for i in range(10):
if i == 5:
break
print(i) # 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
# continue: 현재 반복을 건너뛰고 다음 반복으로
for i in range(10):
if i % 2 == 0:
continue
print(i) # 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
# 중첩 루프에서 break
found = False
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if i * j == 4:
found = True
break
if found:
break
|
[!TIP] 초보자를 위한 팁: break vs continue
- break: “이제 그만! 여기서 끝내고 나가자!” (반복문 전체 종료)
- continue: “이번 건 패스! 다음 순서로 넘어가자!” (현재 반복만 건너뜀)
헷갈린다면 이 문장을 기억하세요!
else 절이 있는 반복문
Python의 독특한 기능으로, 반복문이 정상적으로 종료되면 else 블록이 실행됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| # for-else
for i in range(5):
if i == 10: # 이 조건은 절대 만족하지 않음
break
else:
print("반복문이 정상 종료됨")
# while-else
n = 2
while n < 5:
print(n)
n += 1
else:
print("while 루프 정상 종료")
# break로 종료되면 else 실행 안됨
for i in range(5):
if i == 3:
break
else:
print("이 메시지는 출력되지 않음")
# 실용적 예제: 소수 판별
num = 17
for i in range(2, num):
if num % i == 0:
print(f"{num}은 소수가 아닙니다")
break
else:
print(f"{num}은 소수입니다")
|
🎨 반복문 응용 패턴
리스트 컴프리헨션 (List Comprehension)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| # 기본 형태
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]
print(squares) # [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
# 조건 포함
even_squares = [x**2 for x in range(10) if x % 2 == 0]
print(even_squares) # [0, 4, 16, 36, 64]
# 중첩 반복
matrix = [[i*j for j in range(3)] for i in range(3)]
print(matrix) # [[0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 2], [0, 2, 4]]
# 딕셔너리 컴프리헨션
squares_dict = {x: x**2 for x in range(5)}
print(squares_dict) # {0: 0, 1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9, 4: 16}
# 집합 컴프리헨션
unique_lengths = {len(word) for word in ["apple", "banana", "pear"]}
print(unique_lengths) # {4, 5, 6}
|
중첩 반복문 패턴
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| # 구구단 출력
for i in range(2, 10):
print(f"\n{i}단:")
for j in range(1, 10):
print(f"{i} × {j} = {i*j:2d}", end=" ")
if j % 3 == 0:
print() # 3개씩 줄바꿈
# 2차원 패턴 출력
n = 5
# 직각삼각형
for i in range(1, n+1):
print("*" * i)
# 피라미드
for i in range(1, n+1):
print(" " * (n-i) + "*" * (2*i-1))
|
💡 실전 예제
1. 숫자 맞추기 게임
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| import random
def number_guessing_game():
"""1부터 100까지의 숫자 맞추기 게임"""
secret_number = random.randint(1, 100)
attempts = 0
max_attempts = 10
print("=== 숫자 맞추기 게임 ===")
print(f"1부터 100까지의 숫자를 맞춰보세요! ({max_attempts}번 기회)")
while attempts < max_attempts:
attempts += 1
try:
guess = int(input(f"\n시도 {attempts}/{max_attempts}: "))
except ValueError:
print("올바른 숫자를 입력하세요!")
continue
if guess < 1 or guess > 100:
print("1부터 100 사이의 숫자를 입력하세요!")
continue
if guess == secret_number:
print(f"🎉 정답입니다! {attempts}번 만에 맞추셨네요!")
break
elif guess < secret_number:
print("더 큰 숫자입니다 ⬆️")
else:
print("더 작은 숫자입니다 ⬇️")
else:
print(f"\n😢 실패! 정답은 {secret_number}였습니다.")
# 게임 실행
# number_guessing_game()
|
2. 성적 관리 시스템
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
| def grade_management_system():
"""학생 성적 관리 시스템"""
students = {}
while True:
print("\n=== 성적 관리 시스템 ===")
print("1. 학생 추가")
print("2. 성적 입력")
print("3. 성적 조회")
print("4. 전체 평균")
print("5. 종료")
choice = input("\n선택 (1-5): ")
match choice:
case "1":
name = input("학생 이름: ")
if name in students:
print("이미 등록된 학생입니다.")
else:
students[name] = []
print(f"{name} 학생이 추가되었습니다.")
case "2":
name = input("학생 이름: ")
if name not in students:
print("등록되지 않은 학생입니다.")
continue
try:
score = float(input("성적 (0-100): "))
if 0 <= score <= 100:
students[name].append(score)
print("성적이 입력되었습니다.")
else:
print("0-100 사이의 점수를 입력하세요.")
except ValueError:
print("올바른 숫자를 입력하세요.")
case "3":
name = input("학생 이름: ")
if name not in students:
print("등록되지 않은 학생입니다.")
elif not students[name]:
print("입력된 성적이 없습니다.")
else:
scores = students[name]
avg = sum(scores) / len(scores)
print(f"\n{name} 학생의 성적:")
print(f"점수들: {scores}")
print(f"평균: {avg:.2f}")
if avg >= 90:
grade = "A"
elif avg >= 80:
grade = "B"
elif avg >= 70:
grade = "C"
elif avg >= 60:
grade = "D"
else:
grade = "F"
print(f"학점: {grade}")
case "4":
if not students:
print("등록된 학생이 없습니다.")
else:
all_scores = []
for scores in students.values():
all_scores.extend(scores)
if all_scores:
total_avg = sum(all_scores) / len(all_scores)
print(f"\n전체 평균: {total_avg:.2f}")
print(f"최고점: {max(all_scores)}")
print(f"최저점: {min(all_scores)}")
else:
print("입력된 성적이 없습니다.")
case "5":
print("프로그램을 종료합니다.")
break
case _:
print("잘못된 선택입니다.")
# 시스템 실행
# grade_management_system()
|
3. 패턴 생성기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| def pattern_generator():
"""다양한 패턴을 생성하는 프로그램"""
def print_triangle(n):
"""직각삼각형 패턴"""
print("\n직각삼각형:")
for i in range(1, n+1):
print("*" * i)
def print_inverted_triangle(n):
"""역직각삼각형 패턴"""
print("\n역직각삼각형:")
for i in range(n, 0, -1):
print("*" * i)
def print_pyramid(n):
"""피라미드 패턴"""
print("\n피라미드:")
for i in range(1, n+1):
print(" " * (n-i) + "*" * (2*i-1))
def print_diamond(n):
"""다이아몬드 패턴"""
print("\n다이아몬드:")
# 상단 부분
for i in range(1, n+1):
print(" " * (n-i) + "*" * (2*i-1))
# 하단 부분
for i in range(n-1, 0, -1):
print(" " * (n-i) + "*" * (2*i-1))
def print_number_pattern(n):
"""숫자 패턴"""
print("\n숫자 패턴:")
for i in range(1, n+1):
for j in range(1, i+1):
print(j, end=" ")
print()
# 메인 루프
while True:
print("\n=== 패턴 생성기 ===")
print("1. 직각삼각형")
print("2. 역직각삼각형")
print("3. 피라미드")
print("4. 다이아몬드")
print("5. 숫자 패턴")
print("6. 종료")
choice = input("\n선택 (1-6): ")
if choice == "6":
break
if choice in ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5"]:
try:
size = int(input("크기 입력 (1-20): "))
if 1 <= size <= 20:
if choice == "1":
print_triangle(size)
elif choice == "2":
print_inverted_triangle(size)
elif choice == "3":
print_pyramid(size)
elif choice == "4":
print_diamond(size)
elif choice == "5":
print_number_pattern(size)
else:
print("1-20 사이의 숫자를 입력하세요.")
except ValueError:
print("올바른 숫자를 입력하세요.")
else:
print("잘못된 선택입니다.")
# 패턴 생성기 실행
# pattern_generator()
|
⚠️ 초보자가 자주 하는 실수
1. 들여쓰기 실수
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| # ❌ 잘못된 들여쓰기
if True:
print("에러!") # IndentationError
# ✅ 올바른 들여쓰기 (4칸 권장)
if True:
print("정상")
|
2. == vs = 혼동
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| # ❌ 할당 연산자 사용
if x = 5: # SyntaxError
print("5입니다")
# ✅ 비교 연산자 사용
if x == 5:
print("5입니다")
|
3. 무한 루프 실수
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| # ❌ 무한 루프
i = 0
while i < 10:
print(i)
# i += 1 을 잊음!
# ✅ 올바른 루프
i = 0
while i < 10:
print(i)
i += 1
|
4. 리스트 수정 중 순회
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| # ❌ 순회 중 리스트 수정
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
for num in numbers:
if num % 2 == 0:
numbers.remove(num) # 예상과 다른 결과!
# ✅ 복사본 사용 또는 리스트 컴프리헨션
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# 방법 1: 복사본 순회
for num in numbers[:]:
if num % 2 == 0:
numbers.remove(num)
# 방법 2: 리스트 컴프리헨션
numbers = [num for num in numbers if num % 2 != 0]
|
5. range() 인덱스 실수
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| # ❌ 잘못된 범위
items = ['a', 'b', 'c']
for i in range(len(items) + 1): # IndexError!
print(items[i])
# ✅ 올바른 범위
for i in range(len(items)):
print(items[i])
# 더 좋은 방법
for item in items:
print(item)
|
🎯 핵심 정리
조건문 Best Practices
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| # 1. 간단한 조건은 삼항 연산자 활용
status = "active" if is_logged_in else "inactive"
# 2. 여러 조건 확인시 elif 활용
if condition1:
do_something1()
elif condition2:
do_something2()
elif condition3:
do_something3()
else:
do_default()
# 3. 복잡한 조건은 변수로 분리
is_valid_user = user is not None and user.is_active
is_authorized = user.role in ['admin', 'moderator']
if is_valid_user and is_authorized:
grant_access()
# 4. match 문으로 패턴 매칭 (Python 3.10+)
match status_code:
case 200 | 201:
return "Success"
case 404:
return "Not Found"
case _:
return "Unknown"
|
반복문 Best Practices
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| # 1. 인덱스가 필요하면 enumerate 사용
for i, item in enumerate(items):
print(f"{i}: {item}")
# 2. 여러 리스트 동시 순회는 zip 사용
for name, score in zip(names, scores):
print(f"{name}: {score}")
# 3. 리스트 생성은 컴프리헨션 활용
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10) if x % 2 == 0]
# 4. 무한 루프는 명확한 종료 조건 필요
while True:
if exit_condition:
break
process()
# 5. else 절은 검색 패턴에 유용
for item in items:
if condition(item):
print("Found!")
break
else:
print("Not found")
|
흐름 제어 다이어그램
graph TD
A[시작] --> B{조건문}
B -->|True| C[조건 만족 처리]
B -->|False| D[조건 불만족 처리]
C --> E[반복문 시작]
D --> E
E --> F{반복 조건}
F -->|True| G[반복 처리]
G --> H{continue?}
H -->|Yes| E
H -->|No| I{break?}
I -->|Yes| J[종료]
I -->|No| E
F -->|False| K[else 절]
K --> J
🎓 파이썬 마스터하기 시리즈
📚 기초편 (1-7)
- Python 소개와 개발 환경 설정 완벽 가이드
- 변수, 자료형, 연산자 완벽 정리
- 조건문과 반복문 마스터하기
- 함수와 람다 완벽 가이드
- 리스트, 튜플, 딕셔너리 정복하기
- 문자열 처리와 정규표현식
- 파일 입출력과 예외 처리
🚀 중급편 (8-12)
- 클래스와 객체지향 프로그래밍
- 모듈과 패키지 관리
- 데코레이터와 제너레이터
- 비동기 프로그래밍 (async/await)
- 데이터베이스 연동하기
💼 고급편 (13-16)
- 웹 스크래핑과 API 활용
- 테스트와 디버깅 전략
- 성능 최적화 기법
- 멀티프로세싱과 병렬 처리
이전글: 변수, 자료형, 연산자 완벽 정리 ⬅️ 현재글: 조건문과 반복문 마스터하기 다음글: 함수와 람다 완벽 가이드 ➡️
이번 포스트에서는 프로그램의 흐름을 제어하는 조건문과 반복문을 학습했습니다. 다음 포스트에서는 코드를 재사용 가능하게 만드는 함수와 람다에 대해 자세히 알아보겠습니다. Happy Coding! 🐍✨
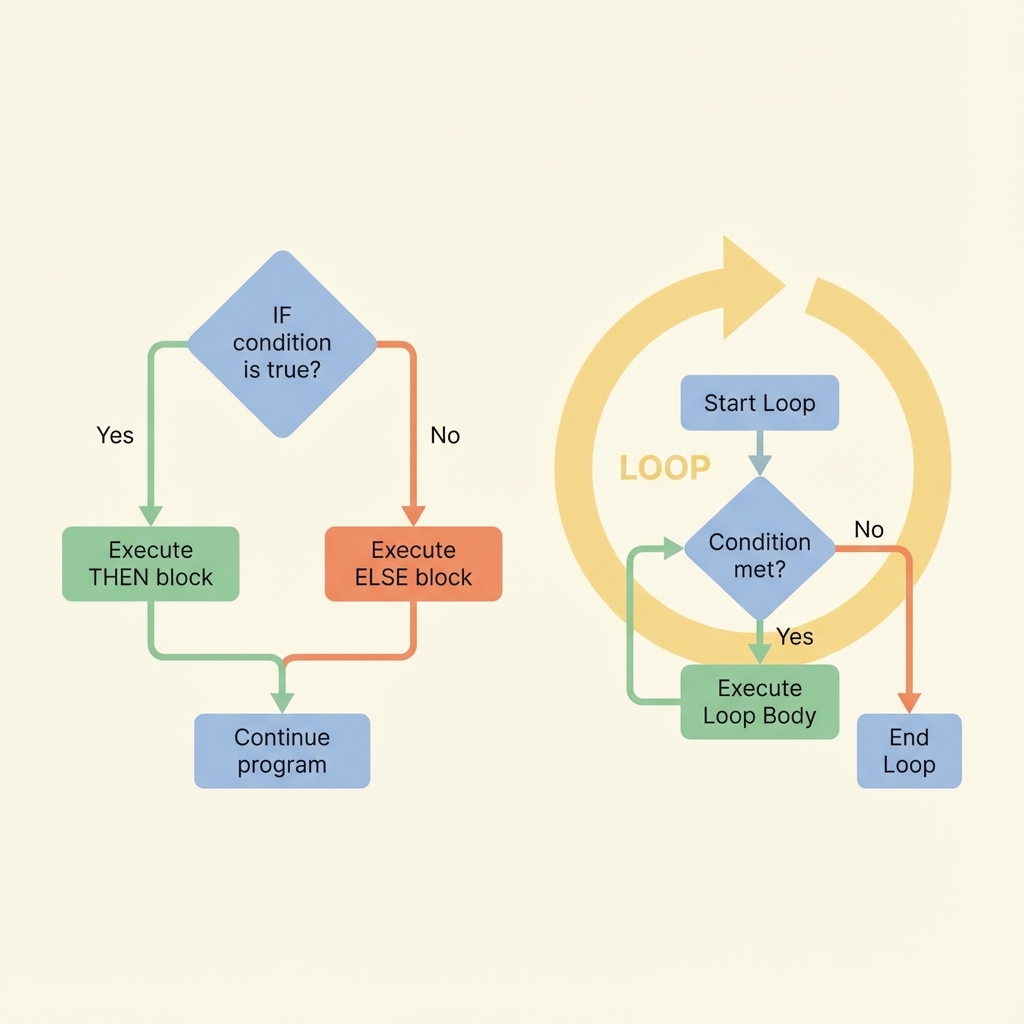 조건문은 갈림길, 반복문은 회전교차로와 같습니다. 프로그램의 흐름을 자유자재로 제어해보세요!
조건문은 갈림길, 반복문은 회전교차로와 같습니다. 프로그램의 흐름을 자유자재로 제어해보세요!